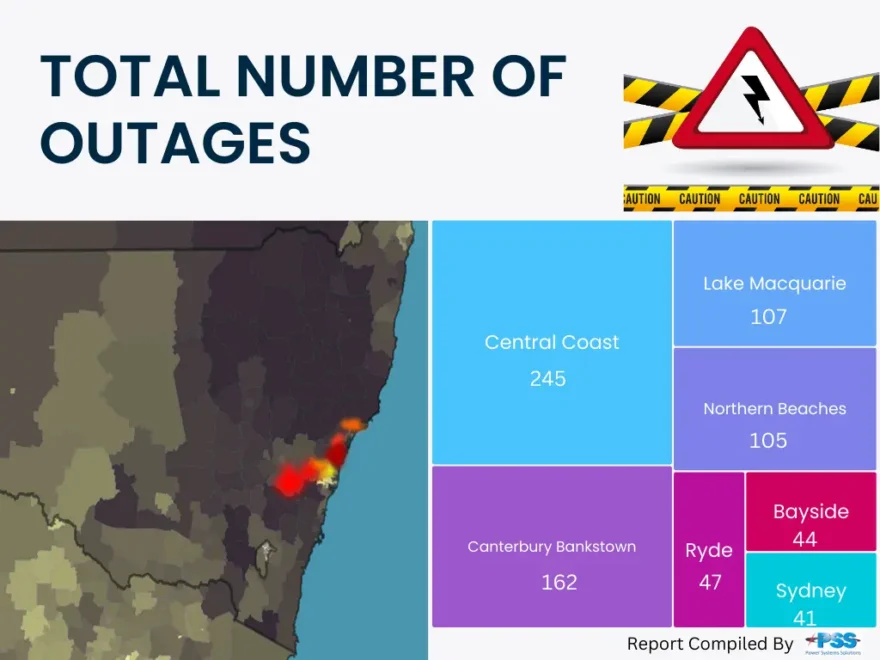
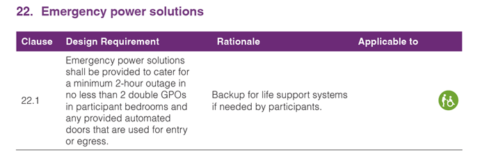
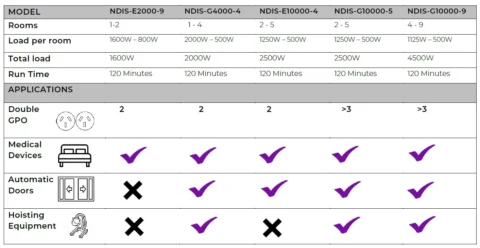
We’re writing to share some exciting news — PSS Distribution is joining Legend Corporation.
Legend is a respected Australian company with trusted brands like CABAC and MSS Data Solutions. This partnership will allow us to offer you a broader range of products and services, while continuing the high standards you’ve come to rely on.
What’s Not Changing at PSS – The Important Stuff
While exciting things are happening behind the scenes, the things that matter most to you stay exactly the same:
- Terrence Daniel remains our dedicated GM, continuing to lead with the same expertise and commitment you trust.
- Existing PSS staff will continue to provide the high quality technical and customer support you’ve come to expect.
- Warranties and service agreements will be fully honoured – nothing changes there.
- And most importantly, our service promise remains rock-solid:
-
- 3 rings – We answer your call within 3 rings
- 3 days – We aim to deliver within 3 days
- 30 minutes – Quotes in 30 minutes or less
The transition will be complete by 1 August 2025.
As part of this transition, we’ll also be moving our pick-up locations into Legend Corporation’s facilities. From 4 August onwards, all order pick-ups will need to be made from the following addresses:
• NSW – 8 Distribution Place, Seven Hills
• WA – 6 Hunt St, Malaga
• VIC – Building 9/621 Whitehorse Rd, Mitcham
Rest assured, PSS’s fast 4-hour turnaround still applies, and our FIS rules remain unchanged.
Thank you to all of our existing customers for their ongoing support — we’re excited about this next chapter and the opportunities it brings.
If you have any questions, please reach out to our team.
Warm regards,
The PSS Distribution Team